 In 2017, nearly 39 percent of total asphalt pavement mix production was produced warm-mix asphalt – a 777-percent increase since 2009. PHOTO: Lone Star Asphalt Paving.
In 2017, nearly 39 percent of total asphalt pavement mix production was produced warm-mix asphalt – a 777-percent increase since 2009. PHOTO: Lone Star Asphalt Paving.Asphalt mix producers continue to make significant use of energy-saving warm-mix asphalt technologies, with more than 99 percent of reclaimed asphalt pavement recycled.
In 2017, 147.4 million tons of warm-mix asphalt was produced at reduced temperatures. That’s nearly 39 percent of total asphalt pavement mix production – and a whopping 777-percent increase since 2009.
Nearly 79 million tons of recycled materials, including shingles, were used in asphalt pavements.
That’s according to the 2018 survey of the U.S. asphalt pavement mixture production industry by the National Asphalt Pavement Association (NAPA). The survey was sponsored by the Federal Highway Administration.
“Through engineering, performance-based specifications, and improved RAP processing, production equipment, and procedures, we are creating asphalt pavement mixtures that successfully incorporate reclaimed and recycled materials,” says NAPA President Mike Acott.
 NAPA President Mike Acott
NAPA President Mike Acott“However, there is still room to improve, and we are supporting research and education efforts to keep the use of these cost effective, environmentally friendly asphalt mixtures growing.”
Asphalt mixture producers from all 50 states completed the 2017 construction season survey, with 238 companies and 1,158 production plants represented.
Since it began in 2009, the survey has documented increases in the use of recycled materials and warm-mix asphalt, though the rapid rate of increase has slowed since 2013, the annual surveys show.
“The results of the asphalt pavement industry survey for the 2017 construction season show that asphalt mixture producers have a strong record of employing sustainable practices and continue to increase their use of recycled materials and warm-mix asphalt (WMA),” the survey says.
“The use of recycled materials, particularly reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) and reclaimed asphalt shingles (RAS), conserves raw materials and reduces overall asphalt mixture costs, allowing road owners to achieve more roadway maintenance and construction activities within limited budgets.
“WMA technologies can improve compaction at reduced temperatures, ensuring pavement performance and long life; conserve energy; reduce emissions from production and paving operations; and improve conditions for workers.”
The report found that WMA technologies have been introduced to reduce production and compaction temperatures for asphalt mixtures, which reduces the energy needed and emissions associated with mixture production.
Additional benefits include improved low-temperature compaction of asphalt mixtures leading to improved pavement performance, as well as a longer paving season.
WMA was chosen for accelerated deployment in federal-aid highway, state department of transportation, and local road projects as part of FHWA’s 2010 Every Day Counts initiative, the report says.
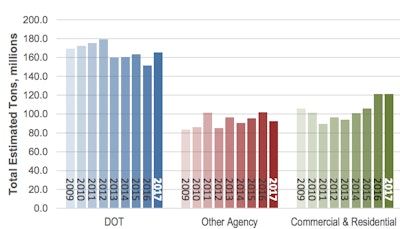 The estimated total HMA/WMA asphalt mixture production by sector, 2009-17. Source: NAPA 2018.
The estimated total HMA/WMA asphalt mixture production by sector, 2009-17. Source: NAPA 2018.
“The asphalt industry remains the country’s most diligent recycler with more than 99 percent of reclaimed asphalt pavement being put back to use,” the survey report says.
“The average percentage of RAP used in asphalt mixtures has increased from 15.6 percent in 2009 to 20.1 percent in 2017.
“In 2017, the estimated RAP tonnage used in asphalt mixtures was 76.2 million tons. This represents more than 3.8 million tons (21.5 million barrels) of asphalt binder conserved, along with the replacement of more than 72 million tons of virgin aggregate.
“Similarly, the use of RAS in asphalt pavement mixtures has increased from 701,000 tons in 2009 to an estimated 944,000 tons in 2017; however, the use of RAS declined significantly (32 percent) from 2016 to 2017” the report says.
The combined savings of asphalt binder and aggregate from using RAP and RAS in asphalt mixtures is estimated at more than $2.2 billion, according to the report authors, Brett A. Williams, Audrey Copeland and T. Carter Ross of NAPA,
“More than 1.4 million tons of other recycled materials were reported as being incorporated into nearly 7.5 million tons of asphalt pavement mixtures during the 2017 construction season, including ground tire rubber, blast furnace slag, steel slag, and cellulose fibers.
“The estimated total production of WMA for the 2017 construction season was 147.4 million tons. This was a 26-percent increase from the estimated 116.8 million tons of WMA in 2016, due largely to increased utilization reported for DOT and commercial and residential tonnage for the year.
WMA utilization in 2017 was 777 percent more than the estimated 16.8 million tons in the 2009 construction season.
“WMA made up 38.9 percent of the total estimated asphalt mixture market in 2017. Production plant foaming, representing nearly 65 percent of the market, is the most commonly used warm-mix technology; chemical additive technologies accounted for a little more than 32 percent of the market,” the report says.
Here are the highlights:
- Asphalt mixture producers remain the country’s most diligent recyclers, with more than 99 percent of asphalt mixture reclaimed from old asphalt pavements being put back to use in new pavements.
- The total estimated tons of RAP used in asphalt mixtures was 76.2 million tons in 2017, representing a 0.91-percent decrease from the 2016 construction season – but also a greater than 36-percent increase from the total estimated tons of RAP used in 2009.
- During the same time frame, total asphalt mixture tonnage increased only 5.9 percent.
- The percentage of producers reporting use of RAP remained at 98 percent of respondents, as it was in 2016. Four producers reported landfilling a small amount (9,595 tons total) of RAP during 2017.
- RAP usage during the 2017 construction season is estimated to have reduced the need for 3.8 million tons (21.5 million barrels) of asphalt binder and more than 72 million tons of aggregate, with a total estimated value of more than $2.1 billion.
- The total estimated amount of RAP stockpiled nationwide at the end of the 2017 construction season was about 102.1 million tons.
- Fractionated RAP represents about 23 percent of RAP use nationwide, and the tons of RAP mixtures produced using softer binders are estimated at 18 percent. while tons produced using recycling agents is estimated at 4 percent.
To see the full 44-page report, click here.










